The Flexibility of GA4’s Data Model

How GA4’s Data Model Enhances Data Collection & Reporting
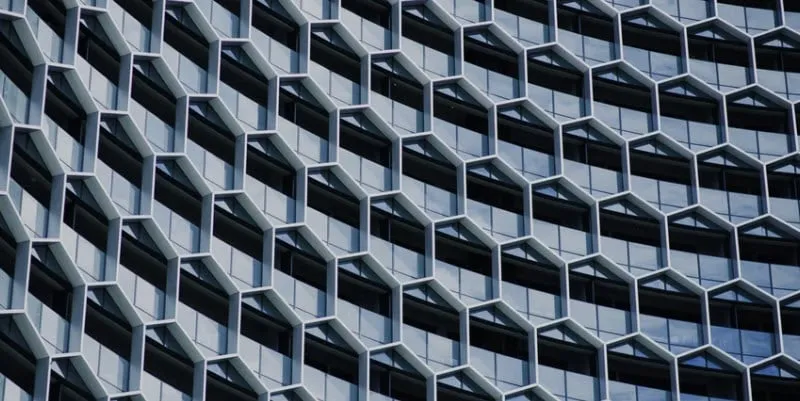
One of the major changes in Google’s latest version of Google Analytics (GA4) is the shift from a session and pageview based model to Firebase’s event based data model.
In GA4, everything is now an event. A pageview is now an event. In Universal Analytics (UA), pageviews and events were separate. This change in the GA4 data model switches the focus from sessions to users and events and brings numerous benefits such as cross platform analysis and the enhanced capacity for funnel and pathing analysis among many others.
In this blog, we will walk you through key differences in the data models of UA and GA4 and the reporting benefits.
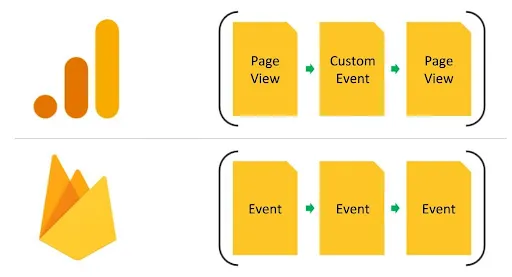
Comparing the UA and GA4 Data Models
The Rigidity of Universal Analytics’ Event Taxonomy
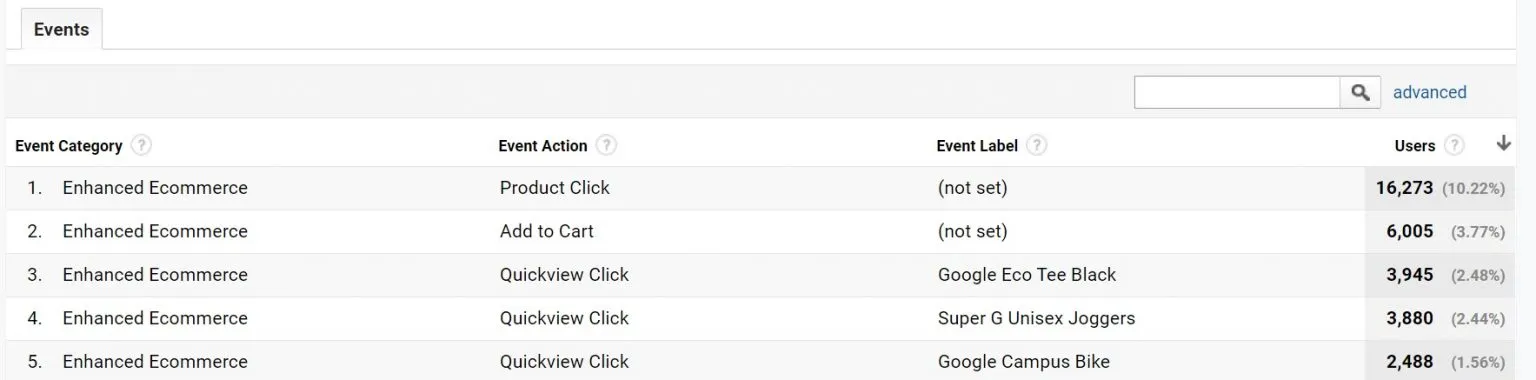
UA events followed a taxonomy of Event Category, Action and Label. While this structure is useful and allows for a sensible naming convention for most events, it does have its drawbacks.
This structure can restrict reporting as typically the event action and label fields require the event category to provide full context.
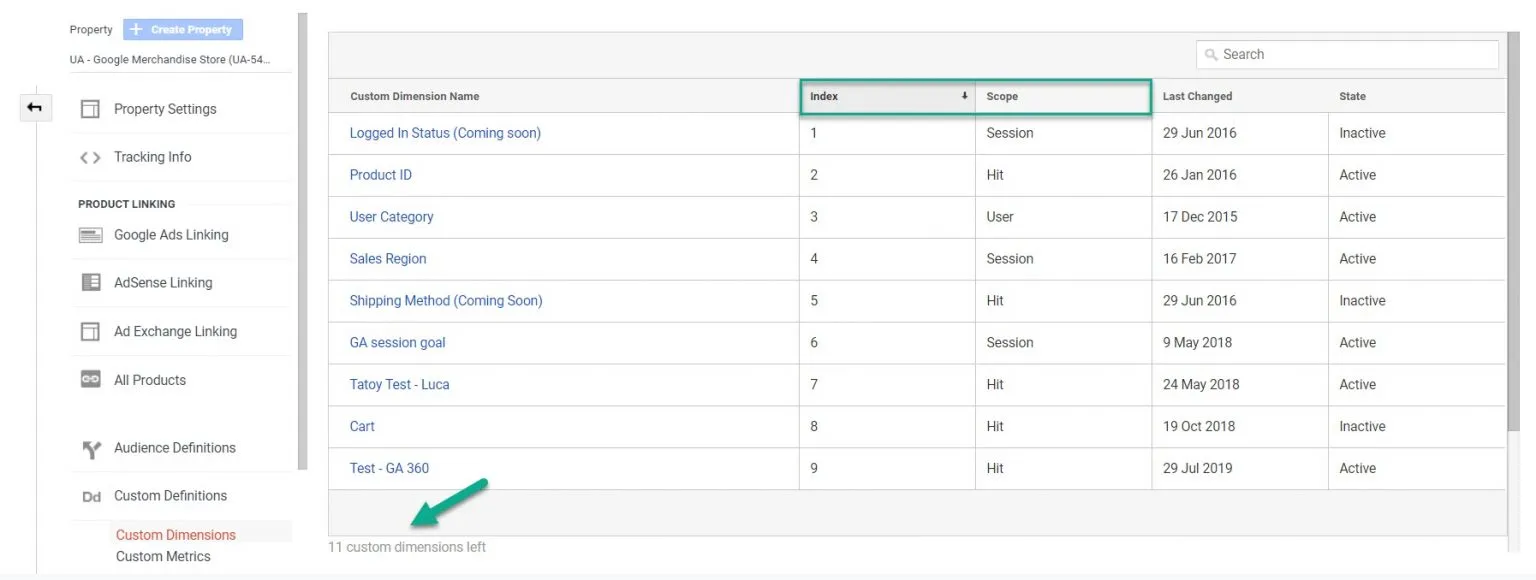
Events often require supplemental information beyond category, action, label in the form of custom dimensions and metrics. While custom dimensions and metrics are incredibly useful, they do need to be implemented and configured correctly. Index numbers have to be matched during configuration and the correct scope needs to be applied. This coupled with the fact that there are only 20 custom dimension and metric slots available per property with the free version of UA means users have to choose what to track wisely.
GA4 Events and Parameters: A Flexible Approach
The restrictive nested taxonomy of events in UA no longer exists in GA4 thanks to it’s event based data model.
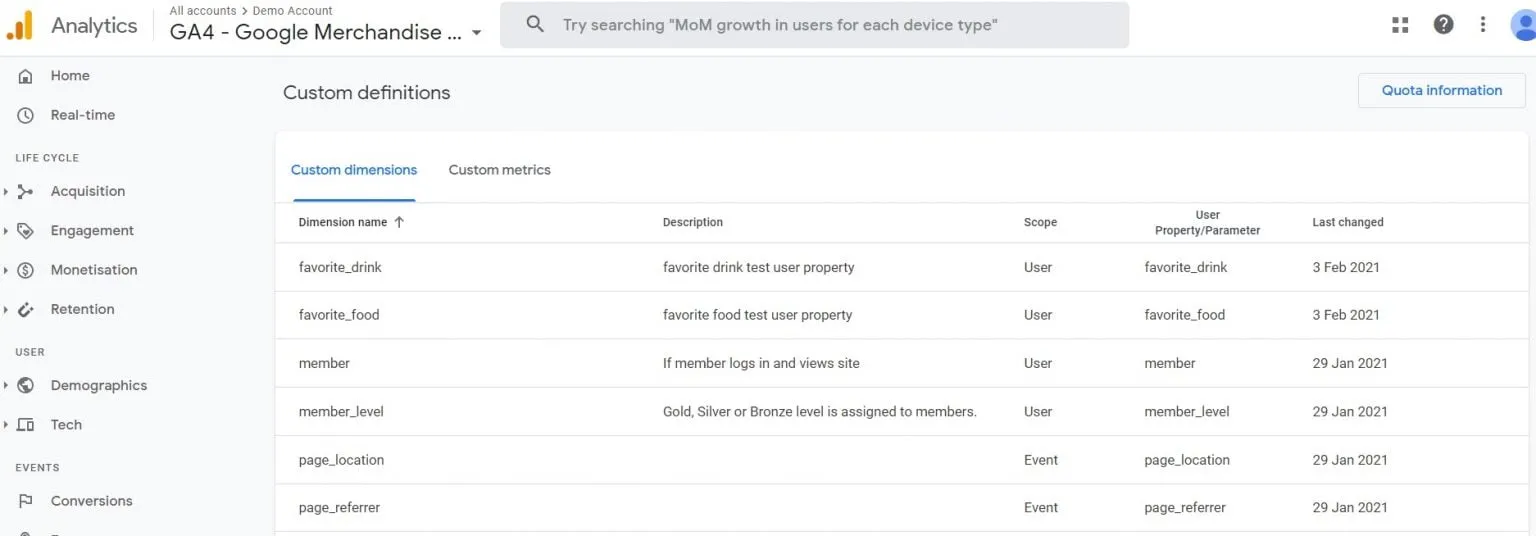
Events in GA4 are distinguished by an event_name parameter and additional parameters in the form of custom dimensions and user properties that describe the event. Event parameters need to be registered in the GA4 interface.
It is possible to add up to 25 parameters per event (and up to 100 parameters per event with GA4 360). GA4 custom parameters are not based on a particular index number. The same parameter can also be used across multiple events, meaning parameters only need to be registered once, saving valuable quota space.
The Reporting Benefits of GA4’s Event Based Data Model
In addition to the added flexibility in data collection, GA4’s data model unlocks and enhances reporting capabilities in particular for funnel and pathing analysis.
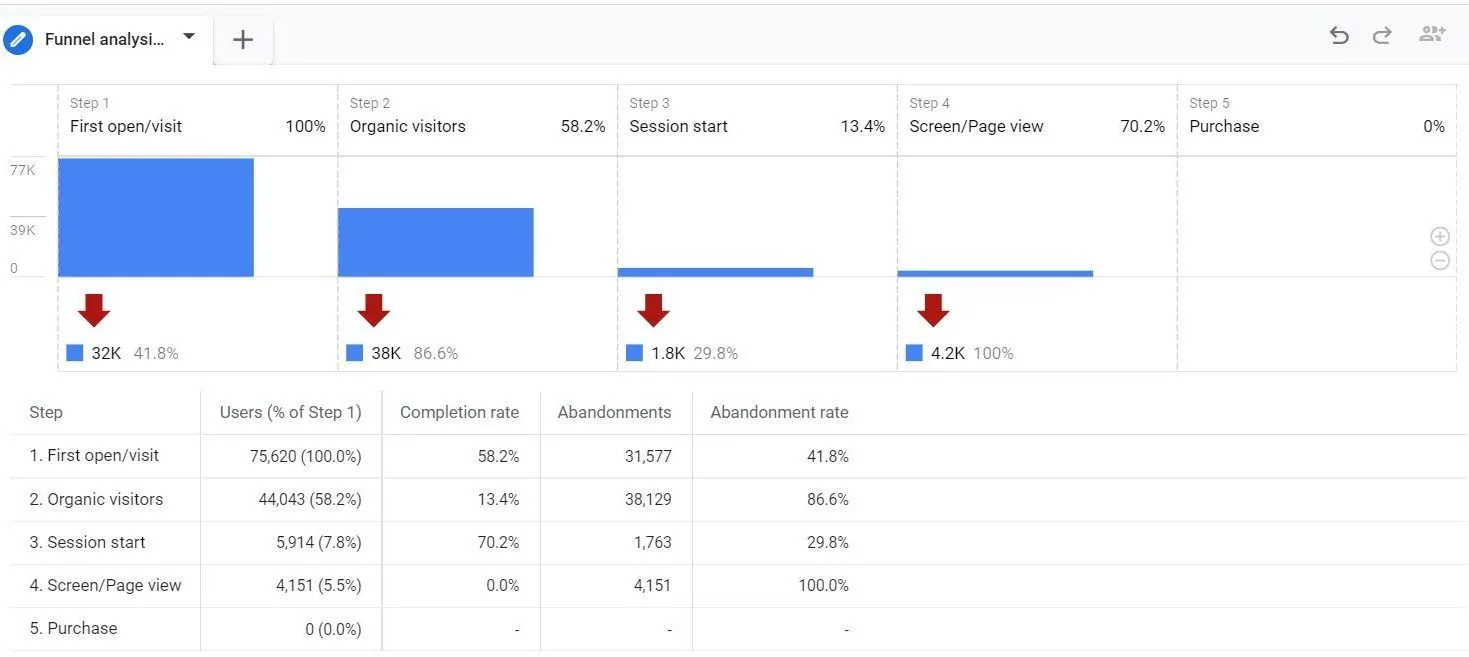
Although Funnel analysis was available in the free version of UA, it was limited to destination goal funnels. Only 360 customers could avail of custom funnels. This is now available to all GA4 users in the analysis hub.
GA4’s data model allows for the stitching and sequencing of both events and pageviews together which greatly enhances users’ ability to ask and answer questions of their data. Any sequence of events can now be captured as steps in a custom funnel.
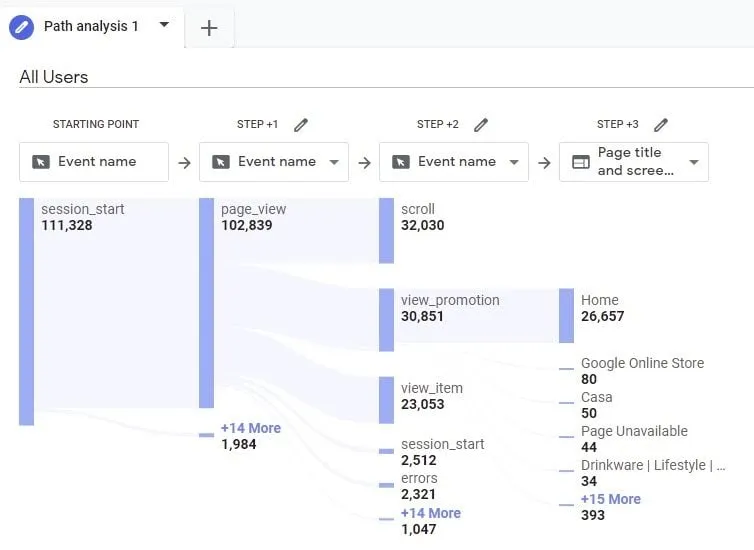
The analysis hub pathing reports are a big leap forward from the Behaviour flow reports in UA. The interface now allows the user to click through various different paths (Up to 10 steps) and paths can be a mixture of both events and pageviews. This greatly expands users’ ability to understand multiple user journeys and behaviours throughout websites and apps.
Do you have questions related to GA4 and its new data model? Let us know in the comments or get in touch! Don’t forget to check out our other GA4 blogs about why you should upgrade to GA4, how to set up a GA4 property and how to create a GA4 property in Data Studio.